[VIPSL]
[Database
& Software]
Database: CT/MR
Image Sequence
[CT]
[MR]
|
| |
 |
 |
|
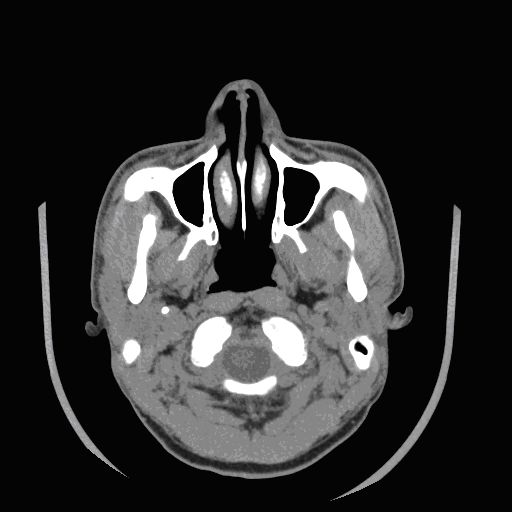
CT Image Sequence:
Based on the variable absorption of x-rays by different
tissues,
a
computed tomography(CT) imaging, also known as "CAT
scanning" (Computerized Axial Tomography)
is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a
combination of x-rays and computer technology to produce
a different form of imaging known as
cross-sectional images (often called slices), both
horizontally and vertically, of the body.
The origin of the word "tomography" is from the Greek
word "tomos" meaning "slice" or "section" and "graphy"
meaning "drawing". A CT imaging system produces
cross-sectional images or "slices" of anatomy, like the
slices in a loaf of bread.
A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body,
including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs.
Spatial and contrast resolution are dependent on the
energy of the x-ray source, slice thickness, field of
view, and scanning matrix.
High resolution CT provides excellent delineation of
osseous structures. |
|
|
|
| |
Its
main limitations are radiation exposure, slightly restricted field of
view, and poor delineation of intrathecal anatomy and pathology.
A CT
image created with an x-ray source is determined by the electron density
of the tissue.
Different
organs have different CT value in CT images. So, their colors will be
different too. In this head CT image, we can see that bones are white
while other parenchyma such as muscles and blood vessels are gray, even
dark.
Many
images slices like this can be combined to give a 3-D view of the head.
And this is what we are bending ourselves to. In the 3-D model of the
head, we shall see something the same as what we see in the
anatomization .
top |
|
| |
 |
 |
|
MR Image Sequence:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an imaging technique
used primarily in medical settings to produce high
quality images of the inside of the human body. MRI is
based on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance
(NMR), a spectroscopic technique used by scientists to
obtain microscopic chemical and physical information
about molecules. The technique was called magnetic
resonance imaging rather than nuclear magnetic resonance
imaging (NMRI) because of the negative connotations
associated with the word nuclear in the late 1970's. MRI
started out as a tomographic imaging technique, that it
produced an image of the NMR signal in a thin slice
through the human body. MRIs are based on totally
different physical properties. An MRI is created when
pulsed radio waves of a specific frequency induce the
transition of a fraction of the spinning protons in the
body into a higher energy state. With the termination of
the radio-frequency pulse, the excited |
|
|
|
| |
nuclei release energy and return to their lower energy state.
Construction of images from this pattern of absorption-release of energy
is called MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging produces superb delineation of
soft tissue structures, excellent characterization of medullary bone,
direct multi-planar imaging, and no radiation exposure.
Computer-generated pictures can show the heart muscle, identify damage
from a heart attack, diagnose certain congenital, cardiovascular defects
and evaluate disease of larger blood vessels such as the aorta. It can
outline the affected part of the brain and help define the problems
created by stroke. In this MRI picture, parenchyma like skin is bright,
but bones are invisible. Like CT images, many slices of this can be
combined to give a 3-D view of the head.
top
Collected by the Medical Video/Image
Engineering Group, July, 2006. |
|
| |
[VIPSL]
[Database
& Software] |
|
|
|
|
|

